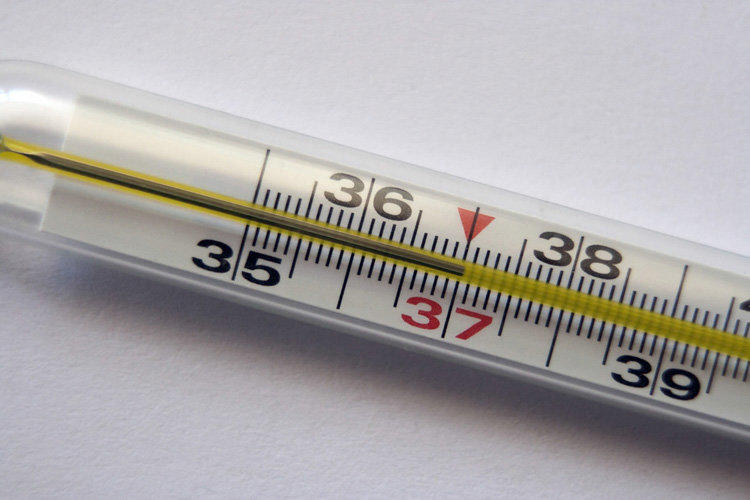
Body temperature is one of the most important physiological parameters indicating the state of the body. We all know from childhood that normal body temperature is +36.6 ºC, and a temperature rise of more than +37 ºC indicates a disease.
- High Temperature Hazard
- Measurement Technique
- Possible causes of prolonged subfebrile
- Variation of the norm
- Pregnancy and lactation
- Thermoneurosis
- Temperature “tails”
- Oncological diseases
- Autoimmune Diseases
- Toxoplasmosis
- Brucellosis
- Tuberculosis
- AIDS
- Worm infestations
- Hidden sepsis, inflammatory processes
- Thyroid Diseases
- Addison’s Disease
- Anemia
- Drug treatment
- Age below one year
- Intestinal diseases
- Hepatitis
- Diagnosis of the causes of long subfebrile
- What should you do if you find a constant fever in yourself or in your child?
High Temperature Hazard
What is the reason for this condition? An increase in temperature is the immune system response to infection and inflammation. The blood is saturated with temperature increasing (pyrogenic) substances produced by pathogenic microorganisms. This, in turn, stimulates the body to produce its own pyrogens. Metabolism is somewhat accelerated to facilitate the immune system fight the disease.
Typically, fever is not the only symptom of the disease. For example, with colds, we feel the typical symptoms for them – fever, sore throat, cough, runny nose. With mild colds, body temperature can be at +37.8 ºC. And for severe infections, such as the flu, it can rise to + 39-40 ºC, with body aches and weakness added to the symptoms.

In such situations, we know very well how to behave and how to treat the disease, because its diagnosis is not a big deal. We rinse our throats, take anti-inflammatory drugs and antipyretic, if necessary, we drink antibiotics, and the disease gradually goes away. And after a few days the temperature returns to normal.
Most of us have encountered this situation more than once in our lives. However, it happens that some people experience several other symptoms. They find that their temperature is elevated compared to normal, but not by much. It is a subfebrile condition — a temperature in the range 37-38 ºC.
Is this condition dangerous? If it does not last long – for several days, and you can associate it with some kind of infectious disease, then no. It is enough to cure it, and the temperature drops. But what if there are no visible symptoms of a cold or flu?
Here it must be borne in mind that in some cases, colds can have degraded symptoms. Infection in the form of bacteria and viruses is present in the body, and immune forces respond to their presence by increasing the temperature. However, the concentration of pathogenic microorganisms is so low that they are unable to cause the typical symptoms of a cold – cough, runny nose, sneezing, sore throat. In this case, the fever may pass after these infectious agents die and the body recovers.
Especially often this situation can be observed during the cold season, during the period of epidemics of colds, when infectious agents can attack the body time and time again, but come across the barrier of alert immunity and not cause any visible symptoms, except for a rise in temperature 37 to 37.5. So if you have 4 days, 37.2 or 5 days, 37.1, while you feel tolerable, this is not a cause for concern.
However, as is well known, colds rarely last more than one week. And, if the fever lasts longer than this period and does not subside, and no symptoms are observed, then this situation is a reason to think seriously. After all, a permanent subfebrile condition without symptoms can be a precursor or a sign of many serious diseases, much more serious than the common cold. These can be diseases of both infectious and non-infectious nature.
Measurement Technique
However, before a serious worrying starts, you should eliminate such a banal cause of subfebrile, as a measurement error. After all, it may well happen that the cause of the phenomenon lies in a faulty thermometer. This often applies to electronic thermometers, especially cheap ones. They are more convenient than traditional mercury, however, they can often show incorrect results. However, mercury thermometers are not safe from errors either. Therefore, it is better to check the temperature on another thermometer.
Body temperature is usually measured in the armpit. Rectal and oral measurements are also possible. In the latter two cases, the temperature may be slightly higher.

Measurement should be carried out while sitting, in a calm state, in a room with a normal temperature. If the measurement is carried out immediately after intense physical excercise or in a overheated room, then the body temperature in this case may be higher than normal. This fact should also be taken into account.
Also body temperature may change during the day. If in the morning the temperature is lower than 37, and in the evening – the temperature is 37 and slightly higher, then this phenomenon may be a variant of the norm. For many people, the temperature may vary somewhat during the day, rising in the evening and reaching values of 37, 37.1. However, as a general rule, the evening temperature should not be subfebrile. In a number of diseases, this syndrome, when the temperature is higher than normal every evening, is also observed. Therefore, in this case, it is recommended to take a medical examination.
Possible causes of prolonged subfebrile
If you have high body temperature without symptoms for a long time, and you do not understand what this means, then you should consult a doctor. Only a specialist can say is it normal or not after thorough examination, and if it’s not – what it may be caused. But, of course, it does not harm to know yourself what can cause such a symptom.
What conditions of the body can cause a long subfebrile state without symptoms:
- variant of the norm
- hormonal changes during pregnancy
- thermoeurosis
- temperature tail of infectious diseases
- oncological diseases
- autoimmune diseases – lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease
- toxoplasmosis
- brucellosis
- tuberculosis
- helminthic invasions
- latent sepsis and inflammatory processes
- foci of infection
- thyroid disease
- drug therapy
- AIDS
- intestinal diseases
- viral hepatitis
- Addison disease
Variation of the norm
Statistics say that 2% of the world’s population has a normal temperature of just over 37. But if you don’t have a similar temperature from childhood, and subfebrile only recently appeared, then this is a completely different case and you don’t fall into this category.

Pregnancy and lactation
Body temperature is regulated by hormones produced in the body. At the beginning of such a period of a woman’s life as a pregnancy, the organism is rearranged, which, in particular, is expressed in an increase in the production of female hormones. This process can cause overheating of the body. Temperatures around 37.3ºC for pregnancy should not cause serious concern. Moreover, the hormonal background is subsequently stabilized, and subfebrile condition disappears. Usually, starting from the second trimester, the woman’s body temperature stabilizes. Sometimes the subfebrile condition can accompany the entire period of pregnancy. If fever is observed during pregnancy, then this situation does not require treatment.
Sometimes a subfebrile condition can also occur with a temperature of about 37.4 in women who are breastfeeding, especially in the first days after the appearance of milk. Here the cause of the phenomenon is similar – fluctuations in hormone levels.
Thermoneurosis
The body temperature is regulated in the hypothalamus – one of the brain sections. However, the brain is an interconnected system and processes in one part of it can influence the other. Therefore, in neurotic states such as anxiety, hysteria the body temperature may rise above 37. The production of an increased amount of hormones also contributes to this. A prolonged subfebrile condition can accompany stresses, neurasthenic states, and many psychoses. Thermoneurosis usually returns to normal during sleep.
To rule out this reason, you should consult with a neurologist or psychotherapist. If you actually have a neurosis or anxiety associated with stress, then you need to undergo a course of treatment, because shaky nerves can cause much greater problems than subfebrileity.
Temperature “tails”
Do not overlook such a banal reason, as a trace of a previously suffered infectious disease. It is no secret that many flu and acute respiratory infections, especially hard ones, lead the immune system to a state of heightened mobilization. And if infectious agents are not completely suppressed, the body can maintain a fever for several weeks after the peak of the disease. This phenomenon is called the temperature tail. It can be observed in both an adult and a child.

Therefore, if the temperature is + 37 ºС and higher and lasts a week, then the causes of the phenomenon may lie precisely in the previously suffered and cured (as it seemed) disease. Of course, if you have been ill shortly before a constant subfebrile temperature is detected by some kind of infectious disease, then there is nothing to worry about – subfebrile is exactly its echo. On the other hand, such a situation cannot be called normal, since it indicates the weakness of the immune system and the need to take measures to strengthen it.
Oncological diseases
This reason also cannot be discounted. Often it is subfebrile that is the earliest sign of a developing tumor. This is explained by the fact that the tumor throws pyrogens into the bloodstream – substances that cause a rise in temperature. Especially often subfebrile condition accompanies blood cancer – leukemia. In this case, the effect is caused by a change in the blood composition. To exclude such diseases, it is necessary to undergo a thorough examination and a blood test. The fact that persistent fever can be caused by such a serious illness as oncology makes us take this syndrome seriously.
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases are caused by an abnormal reaction of the human immune system. In normal state immunity cells – phagocytes and lymphocytes attack foreign bodies and microorganisms. However, in some cases, they begin to perceive the cells of their own body as alien, which leads to the appearance of the disease. In most cases, connective tissue is affected.
Virtually all autoimmune diseases – rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Crohn’s disease, are accompanied by fever up to 37 and above without symptoms. Although these diseases usually have a number of manifestations, they may be invisible at an early stage. To exclude such diseases, you must be examined by a doctor.
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a very common infectious disease, which often occurs without noticeable symptoms, with the exception of fever. Exposed to the disease often are pet owners, especially cats, which are carriers of bacilli. It means that if you have fluffy pets living at home and the temperature is subfebrile, then this is reason to suspect this disease. Also, the disease can be infected through poorly roasted meat. To diagnose toxoplasmosis, you should have a blood test for infection. You should also pay attention to symptoms such as weakness, headaches, loss of appetite. The temperature during toxoplasmosis is not strayed with antipyretic drugs.
Brucellosis
Brucellosis is another disease caused by infection transmitted through animals. But this disease often affects farmers dealing with livestock. The disease in the initial stage is expressed in a relatively low temperature. However, as the disease progresses, it can take on severe forms, affecting the nervous system. But if you are not working on a farm, brucellosis as a cause of hyperthermia can be excluded.
Tuberculosis
Alas, phthisis, notorious for works of classical literature, has not yet become history. Tuberculosis currently affects millions of people. And this disease is now typical not only for penetentiary facilities as many believe. Tuberculosis is a severe and persistent infectious disease that is difficult to treat even with modern medicine.
However, the effectiveness of treatment depends largely on how quickly the first signs of the disease were detected. The most early signs of the disease include subfebrile condition without other clearly expressed symptoms. Sometimes temperatures above 37 ºC can be observed not all day, but only in the evening. Other symptoms of tuberculosis include excessive sweating, fatigue, insomnia, and weight loss. To accurately determine whether you have tuberculosis, you must perform an analysis for tuberculin (Mantoux test), and also make a fluorography. It should be borne in mind that fluorography can only reveal the pulmonary form of tuberculosis, while tuberculosis can also affect the urogenital system, bones, skin and eyes. Therefore, you should not rely only on this diagnostic method alone.
AIDS
20 years ago, the diagnosis of AIDS meant a certain death. Now the situation is not so sad – modern medications can support the life of a person infected with HIV for many years or even decades. To infect with this disease is much easier than is commonly believed. This disease affects not only the representatives of sexual minorities and drug addicts. You can pick up an immunodeficiency virus, for example, in a hospital during blood transfusions, during casual sexual contact.
Persistent low-grade fever is one of the first signs of illness. Note, that in most cases, the weakening of immunity in AIDS is accompanied by other symptoms – an increased susceptibility to infectious diseases, rashes on the skin, impaired stool. If you have a reason to suspect AIDS, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Worm infestations
Helminths is a common name of parasitic worms living in the human body. To become infected with parasites is not so difficult, because the eggs of many of them live in animals, in the ground or in water bodies. Not following the rules of hygiene leads to the fact that they enter the human body. Many parasitic diseases can cause persistent low-grade fever. Usually, it is accompanied by indigestion, but in many cases, especially if the parasites have settled not in the intestine, but in other tissues, these symptoms may not be present. You should also pay attention to such a frequent symptom as weight loss. Intestinal parasites are detected by stool analysis. Also, many parasitic diseases are diagnosed with a blood test.
Hidden sepsis, inflammatory processes
Often an infection in the body can be hidden, and not show any signs other than high temperature. Foci of sluggish infectious process can be located in almost any organ in the cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, in the bone and muscle systems. The organs of urination (pyelonephritis, cystitis, urethritis) are most often subject to inflammation. Often subfebrile condition can be associated with infective endocarditis – a chronic inflammatory disease affecting the surrounding tissue of the heart. This disease may for a long time be hidden and not manifest itself in any other way.
Also, special attention should be paid to the oral cavity. This area of the body is especially vulnerable to the effects of pathogenic bacteria, since they can enter it regularly. Even simple, untreated caries can become a focus of infection, which will enter the bloodstream and cause a permanent protective response of the immune system in the form of fever. The risk group also includes patients with diabetes mellitus who may have non-healing ulcers, which manifest themselves through an elevated temperature.
Thyroid Diseases
Thyroid hormones, such as thyroid-stimulating hormone, play an important role in regulating metabolism. Some diseases of the thyroid gland can increase the release of hormones. Increasing the amount of hormones may be accompanied by symptoms such as increased heart rate, weight loss, hypertension, inability to tolerate heat, deterioration of hair and fever. Nervous disorders are also observed – increased anxiety, anxiety, confusion, neurasthenia.
Temperature increases can also occur with a lack of thyroid hormones.
To eliminate the imbalance of thyroid hormones, it is recommended to have a blood test for thyroid hormone levels.
Addison’s Disease
This disease is quite rare and is expressed in a decrease in hormone production by the adrenal glands. It develops for a long time without any special symptoms and is also often accompanied by moderate fever.
Anemia
A slight fever may also cause a syndrome such as anemia. Anemia is called lack of hemoglobin or red blood cells in the body. This symptom can manifest itself in various diseases, especially it is characteristic of severe bleeding. Also, an increase in temperature can be observed with some avitaminosis, iron deficiency and hemoglobin in the blood.
Drug treatment

Subfebrile temperature also may be caused by medications. Many medicines can cause fever. These include antibiotics, especially penicillin drugs, some psychotropic substances, in particular, antipsychotics and antidepressants, antihistamines, atropine, muscle relaxants, narcotic analgesics. Very often, an increase in temperature is a form of an allergic reaction to a drug. This version is probably the easiest to check – just stop taking the medicine that causes suspicion. Of course, this should be done with the permission of the attending physician, since the abolition of the drug can lead to much more serious consequences than subfebrile.
Age below one year
In infants, the causes of subfebrile temperature may lie in the natural processes of development of the body. Commonly, a person in the first months of life has body temperature slightly higher than adults. In addition, infants may experience a violation of thermoregulation, which results in a low subfebrile temperature. This phenomenon is not a symptom of pathology and should go away by itself. Although with increasing temperature in infants, it is still better to show them to the doctor to rule out infections.
Intestinal diseases
Many infectious intestinal diseases can be asymptomatic, except for a temperature increase above normal values. Also, this syndrome is typical for some inflammatory processes in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, for example, in ulcerative colitis.
Hepatitis
Hepatitis B and C variants – severe viral diseases affecting the liver. As usual, long subfebrile condition accompanies sluggish forms of the disease. However, in most cases it is not the only symptom. Typically, hepatitis is also accompanied by heaviness in the liver, especially after eating, yellowness of the skin, pain in the joints and muscles, and general weakness. If you suspect that you have hepatitis, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible, because promptly initiated treatment reduces the likelihood of serious life-threatening complications.
Diagnosis of the causes of long subfebrile
As you can see, there is a large number of potential causes that can lead to a violation of the body’s thermal control. And finding out why it happens is not easy. This can take a lot of time and require considerable effort. However, there is always a reason to this condition. And the fever is always talking about something, usually that there is something wrong with the body.
Often, it is impossible to establish the exact cause of subfebrile at home. However, some conclusions about its nature can be made. All the reasons that cause fever can be divided into two groups – associated with some inflammatory or infectious process and not associated with it. In the first case, the intake of antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs, such as aspirin, ibuprofen or paracetamol, is able to restore the normal temperature, albeit briefly. In the second case, taking such drugs won’t make any effect. However, one should not think that the absence of inflammation makes the cause of subfebrile less serious. On the contrary, serious things like cancer can be among the non-inflammatory causes of subfebrile temperature.
There is a small number of diseases which have fever as a single symptom. In most cases, there are other symptoms – for example, pain, weakness, sweating, insomnia, dizziness, hypertension or hypotension, impaired pulse, abnormal gastrointestinal or respiratory symptoms. However, these symptoms are often degraded, and the common man is usually unable to determine the diagnosis from them. But for an experienced doctor, the picture may be clear. In addition to the symptoms, you should tell your doctor what actions you have recently performed. For example, did you communicate with animals, what products did you eat, did you travel to exotic countries, etc. When determining the cause, information about the patient’s previous diseases is also used, because it is quite possible that subfebrile is due to a relapse of some long-cured disease.
To establish or clarify the causes of subfebrile, it is usually necessary to pass several physiological tests. First of all, it is a blood test. In the analysis results one should pay attention to such a parameter as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. An increase in this parameter indicates an inflammatory process or infection. Parameters such as white blood cell count, hemoglobin levels are also important.
To detect HIV, hepatitis it requires special blood tests. Urinalysis is also needed to help determine if there are inflammatory processes in the urinary tract. It also draws attention to the number of leukocytes in the urine, as well as the presence of protein in it. To eliminate the possibility of helminthic invasions, feces are analyzed.
If the analysis does not allow us to unambiguously determine the cause of the anomaly, then internal organs are examined. For this, various methods can be applied – ultrasound, radiography, computed and magnetic tomography.
A chest X-ray can help identify the pulmonary form of tuberculosis, and an ECG can help identify infective endocarditis. In some cases biopsy may be indicated.
Diagnosing a subfebrile condition can often be complicated by the fact that the patient may have several potential causes of the syndrome, but it is not always easy to separate the true causes from the false ones.
What should you do if you find a constant fever in yourself or in your child?
Which doctor treat this symptom? The easiest way is to go to a therapist, and he, in turn, can give direction to specialists – an endocrinologist, an infectious diseases specialist, a surgeon, a neurologist, a otolaryngologist, a cardiologist, etc.
Of course, subfebrile temperature, unlike febrile, is not dangerous for the body and therefore does not require symptomatic treatment. Treatment in such a case is always aimed at eliminating the hidden causes of the disease. Self-medication, for example, with antibiotics or antipyretic, without a clear understanding of the actions and goals is unacceptable, since it can not only be ineffective and blur the clinical picture, but also lead to the fact that the real cause will stay unattended.
But from the insignificance of the symptom it does not follow that one should not pay attention to it. On the contrary, low-grade fever is a reason to undergo a thorough examination. This step should not be put off until later, reassuring ourselves that this syndrome is not harmful to health. It should be understood that such a seemingly insignificant disruption of the body’s work could be serious problems.