- Causes of pharyngitis
- Pharyngitis: symptoms of the disease
- Signs of the acute stage
- Symptoms for chronic form
- Manifestations depending on the causative agent of the disease
- Differential diagnosis of pharyngitis: symptoms, treatment of similar diseases
- Pharyngitis: treatment of acute and chronic forms of the disease
- Comprehensive treatment of pharyngitis
- Treatment of pharyngitis in chronic form
What is pharyngitis? This is a disease in which the inflammatory process in the pharynx affects its mucous membrane and lymphoid tissue. Symptoms of pharyngitis are similar to other diseases of the pharynx: sore throat, tingling sensation, dry surface cough. Untimely or improper treatment of pharyngitis is dangerous by the transition to the chronic form of the disease, severe complications, the spread of infection in the body and damage to other tissues and organs. It is necessary to distinguish diseases similar in symptomatology and methods of their treatment, so, in case of a sore throat, they can speak of pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis and other diseases and their combinations.
Causes of pharyngitis
The disease is caused by various factors. Most pharyngitis have an infectious etiology, the process develops under the influence of an infectious agent. Among the most frequent pathogens of the acute form of the disease are:
- viruses (parainfluenza, adenovirus, rhinovirus, cytomegalovirus, enterovirus, coronavirus, influenza viruses, herpes simplex, Epstein-Barr, Coxsackie, HIV, etc.,
- pathogenic microorganisms: staphylococcus of different groups, pneumococcus, hemophilus bacillus and others;
- fungi, most often of the genus Candida;
- specific forms of the disease are possible with the defeat of the pharynx gonococcus, chlamydia.
With group effects on the pharyngeal mucosa of various infectious agents, they speak about the association of pathogens: viral-bacterial, viral-fungal, etc. Such forms of the disease require combination therapy.
Among the causes of the acute form of the disease, pharyngitis of allergic etiology, diseases arising from exposure to irritating factors of a chemical or physical nature (internal and external injuries of the pharynx area) of nature, also stand out.
A prolonged inflammatory process of the pharyngeal mucosa provokes the development of a chronic form of the disease. Factors contributing to the occurrence of chronic forms include the following groups:
- frequent diseases of the nasopharynx of a bacterial nature (“colds”), Frequent or chronic diseases of the nasopharynx (sinusitis, tonsillitis) and oral cavity (caries, stomatitis, gingivitis, etc.), lack of hygiene;
- prolonged or permanent exposure of the pharyngeal mucosa to chemical irritants due to bad habits, working in adverse conditions, living in a locality with environmentally harmful production, non-compliance with the rules of handling household or construction chemicals, some diseases. The most common irritants include tobacco smoke, alcohol, evaporation of paints and varnishes, chlorine-containing materials, some topical medications, stomach contents during gastroesophageal reflux, frequent vomiting, regurgitation, etc.;
- physical impact on the pharynx with frequent use of spicy, hot, cold food, inhalation of hot, excessively dry, cold air, air masses with inclusions (dust, fine particles of materials, sand);
- long-term allergic reaction, most often with pollinosis or an allergy to domestic animals, dust mite;
- professional factor: constant tension of the muscles of the pharynx with lecturers, speakers, singers, guides, teachers, etc.
- Endocrine disorders and diseases associated with Sjogren’s syndrome: insufficient production of salivary glands, causing drying of the pharyngeal mucosa.
Pharyngitis: symptoms of the disease
Depending on the form of the disease, the symptoms may also vary.
Signs of the acute stage
The first symptom of the disease is discomfort in the throat. With increasing symptoms in the clinical picture are observed:
- tickling sensation, dry pharyngeal mucosa, throat “scratches”, “sores”; sore throat;
- discomfort when swallowing;
- dry cough, which increases pain in the throat;
- puffiness, hyperemia of the posterior pharyngeal wall, palatine arches;
- inflammation of lymphoid grains, with bacterial etiology of the disease – the formation of mucopurulent plaque on them;
- irradiation of pain in the ear, ear canals;
- enlarged cervical, occipital, submandibular lymph nodes, tenderness on palpation;
- General signs of indisposition: weakness, deterioration of health, headache, fever.
With the development of complications, otitis, mastoiditis, sinusitis, purulent tonsillitis, purulent lymphadenitis may join, and purulent abscesses may form in the pharynx.
Symptoms for chronic form
The chronic form of the disease is divided into several types:
-
- granular or hypertrophic appearance;
- atrophic or subatrophic;
- mixed type;
- catarrhal chronic form.
The chronic form of the disease occurs without marked signs of deterioration of well-being. The main symptom is discomfort in the throat area: tickling, a feeling of dryness, a foreign body in the throat, an obsessive dry cough without mucus. In the throat, there is a cluster of viscous sputum.
When atrophic pharyngitis develops the process of thinning the mucous membrane, its drying. Visually inspecting the effect of “varnished surface” with the inclusion of dried crusts. Hypertrophic chronic form is manifested by the proliferation of lymphoid tissue on the back of the pharynx and / or an increase in tubopharyngeal ridges.
With exacerbation of the chronic course of the disease, the symptoms are complemented by hyperemia, edema, deterioration of health.

Manifestations depending on the causative agent of the disease
Much of the typical and / or specific manifestations of the disease depend on the type.
infectious agent or another reason for the development of the inflammatory process.
| Infectious agent | Symptomatics |
| Rhinovirus | Rhinitis combined with mild sore throat |
| Adenovirus | Painful sensations, addition of purulent tonsillitis, conjunctivitis, formation of pharyngeal abscesses |
| Streptococcus | Febrile hyperthermia, the spread of the inflammatory process on the tongue, the palatine arches, pronounced swelling of the mucous |
| Flu viruses | Symptoms of intoxication, fever |
| human herpes simplex virus | Stomatitis, herpes sores in the mouth, on lips |
| Coxsackie Virus | Herpangina, vesicular rash on the back of the throat, severe pain |
| Epstein-Barr virus | Clinical picture of infectious mononucleosis with persistent sore throat, marked swelling of the pharyngeal mucosa, purulent-mucous secretions from the lacunae, lymphadenopathy |
For any etiology of pharyngitis, symptoms and treatment should be evaluated and prescribed by a specialist.
Differential diagnosis of pharyngitis: symptoms, treatment of similar diseases
The disease requires differentiation due to the similarity of symptoms and possible adherence of inflammatory processes in other parts of the pharynx. With the same sensations, the diseases can have different etiologies, a lesion area, a course and complications. So, in the presence of a sore throat, patients can talk about pharyngitis, and specialists share pharyngitis and tonsillitis, laryngitis, as well as mixed diagnoses (laryngopharyngitis, pharyngitis). Symptoms and treatment can be very close both in clinical manifestations and in therapy methods, however, it is necessary to consult a specialist in each case to diagnose the disease and receive appointments. Attempts of self-diagnosis, clarification of differences in tonsillitis from laryngitis, forms and causes of pharyngitis, “what it is and how to treat it” can lead to a deterioration of the condition, the transition of the disease into a chronic form, the development of serious complications.
Primary diagnosis is carried out by an ENT doctor with the help of a visual examination of the patient’s mouth and throat, anamnesis, and analysis of the patient’s complaints. If visual inspection is not enough, use the instrumental method in good light.
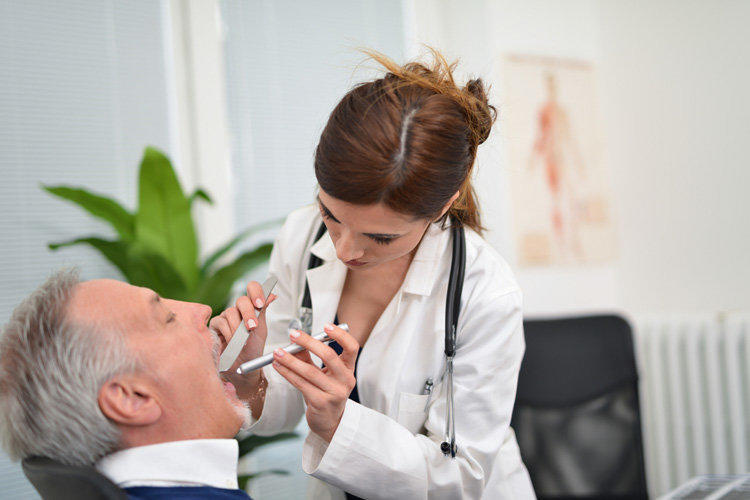
To identify the causative agent and the cause of the disease, a microbiological smear test, a blood test for the presence of antibodies to streptococcus, general indicators, and urinalysis for sugar are carried out. If you suspect a chronic inflammatory process, the diagnosis is carried out by the method of endoscopic examination of the larynx, pharynx and nasal cavity.
Pharyngitis: treatment of acute and chronic forms of the disease
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. The priority is to exclude factors that irritate the mucous membranes of the pharynx: spicy, sour, salty foods, excessively hot and cold foods, drinks, smoking, alcohol, vocal cord tension, being in a smoky, polluted space, etc.
It is advisable to purirovat food before use, exclusion of dishes that can injure the inflamed mucosa (nuts, seeds, crackers, etc.). Drinking regimen – at least 1.5-2 liters of fluid per day, preferably unsweetened compotes, diluted fruit drinks, dogrose broth in a heated form, herbal teas.
General recommendations for maintaining the temperature in the room where the sick person is located, within 21-22 ° C, and humidity not less than 60%. The patient is recommended to refrain from physical exertion, excessive activity, loads. Bed rest is prescribed when there is a pronounced clinical picture of intoxication of the body, severe course of the disease, general weakness of the body.

Comprehensive treatment of pharyngitis
Drug treatment of pharyngitis is carried out with the dynamic observation of a physician. The prescription of drugs of local and general action, auxiliary therapeutic procedures has two directions: reduction of local inflammatory or allergic reaction, reduction of mucosal edema, and active influence on the causes of the disease (with the proven presence of pathogenic microorganisms in the etiology of the disease).
There are several groups of drugs used in this disease:
- anti-inflammatory, antiseptic agents of local action (solutions for rinsing, inhalation, lubrication of the pharyngeal mucosa, sprays, tablets and other forms of resorption drugs);
- local or general pain medication
- if necessary: antipyretics, antibiotics, antivirals, local immunostimulants, etc.
In acute pharyngitis, the symptoms of which are expressed in a bright form, it is recommended to take combined anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs in the form of sprays or aerosols (Stopangin, Antiangin, Strepsils, Faringosept). Tablets, lozenges, lozenges for sucking are used for mild disease.
Regular (3-5 times a day) gargling is considered the most important and highly effective treatment for the acute form of the disease. You can use ready-made antiseptic solutions, decoctions of herbs (calendula, chamomile, peppermint), salt solutions, a combination of baking soda and salt, etc. The greatest therapeutic effect is achieved with a combination of antiseptics and soda-salt solutions, but the number and duration of rinses and not the composition of the solutions.
Inhalation methods are also used to treat the disease. With this disease, it is possible to use both modern nebulizers and inhalers, as well as old methods of vapor inhalation over a container with a hot decoction of herbs, since the penetration of vapor particles into the lower respiratory tract is not required. Important: when choosing drugs for inhalation, you should consult with your doctor, otherwise you should limit yourself with saline or mineral water. When inhaling steam above a container with a decoction of herbs, one should be aware of possible allergies to some medicinal plants, limit the temperature of the liquid and not use this method at elevated body temperature.
Treatment of pharyngitis in chronic form
Treatment of chronic forms of any disease is a long process. Symptoms and treatment of chronic forms depend on the cause of the disease. Speaking of “pharyngitis” as an insignificant disease, delivering a little discomfort, it is worth remembering that it can cause complications and serious consequences, both local and systemic, due to the constant presence of inflammation in the body.
For effective therapy, it is necessary to eliminate the cause of pharyngitis (associated diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, foci of infection in the nasopharynx, oral cavity, endocrine disorders, exposure to occupational, occupational hazards, negative factors of smoking, etc.).
In addition to the general procedures of regular rinsing, irrigation of the mucous membranes, taking anti-inflammatory drugs, treatment is also aimed at eliminating established pathologies.
In the case of a hypertrophic form, the growth of lymphoid tissue requires correction by exposure to electric current or cold (electrocoagulation, cryotherapy).
Atrophic form requires regeneration procedures, hydration of the mucous membrane, stimulation of the mucus secretion process. Used lubrication solution of Lugol in glycerin, vitamin therapy (preparations of vitamin A, ATP).
For the treatment of chronic forms, various physiotherapy procedures are recommended, such as electrophoresis, inductothermia, magnetic and laser therapy, and ultraviolet irradiation of the nasopharynx. When treating the chronic form, it is recommended to stay in sanatoriums of the corresponding orientation.