We know perfectly well that omega-type fatty acids are essential for normal body function, hair and nail beauty, excellent well-being and balanced nutrition. But few know that omega-3 fatty acids that can be found in salmon are not limited here.
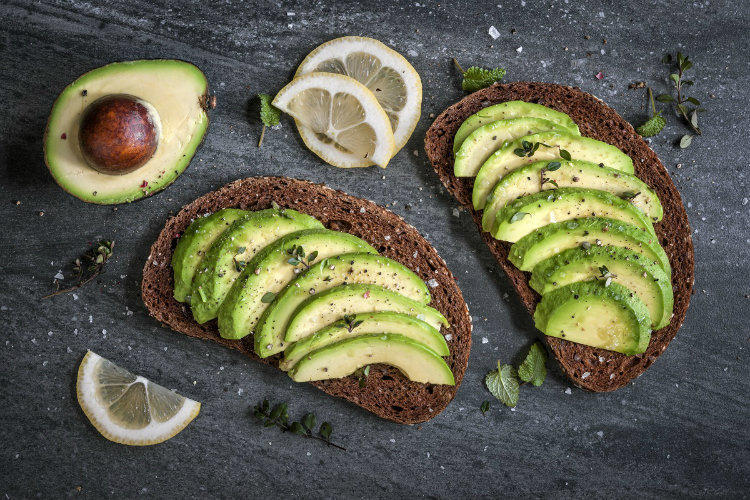
In fact, there are three types of omega acids: omega-3, omega-6 and omega-9. And, for example, omega-9 acids, which are contained in avocados, are very different from omega-3 acids contained in fatty fish. Below is all you need to know about these certainly useful, but such different elements.
What is omega fatty acids
Quick chemistry lesson: fats are a kind of brick walls that are made up of fatty acids. All fatty acids have an even number of carbon atoms that are attached to each other along a chain. Some of them have simple bonds between carbon atoms and are called saturated fats, while others have double bonds and are considered unsaturated. Omega-3, omega-6 and omega-9 are all types of natural unsaturated fats, which most experts in the field of healthy nutrition consider to be much more beneficial than saturated fats.
And back to the chemical structure: the beginning of the carbon chain is called alpha, and its end is called omega. Omega-3 acids have a triple in the title, because the first molecule with a double bond is three carbon atoms from the omega-end (the same with omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids). So, with the boring theory figured out – it’s time to go to the knowledge that you can apply in practice.
Omega-3: what’s the use and where to get it
Experts warn that our body does not know how to produce omega-3 fatty acids, so it is necessary to eat foods rich in omega-3, or take supplements to avoid their deficiency. There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
EPA and DHA are found in oily fish, such as salmon, mackerel, and herring. EPA has a powerful anti-inflammatory effect and, according to research, can reduce the risk of heart disease, rheumatism and cancer. At the same time, DHA plays an important role for brain health. The optimal amount of omega-3 is two to three servings of fatty fish per week. At the same time, ideally, a quarter of all the fats you consume should contain omega-3 fatty acids.
Omega-6: what’s the use and where to get it
As in the case of omega-3 fatty acids, our body is not able to produce them independently. However, you can get enough omega-6 from your diet – and you should use it. These acids are mainly found in vegetable oils, such as corn oil, safflower oil, sesame oil, peanut oil and soybean oil.
But be careful: while omega-6s play an important role in the body, if there are too many of them, it can cause inflammation. (Interestingly, most people get 15-25 times more omega-6 fatty acids from omega-3 from their diet).
Omega-9: what’s the use and where to get it
Unlike omega-3 and omega-6, omega-9 fatty acids are considered insignificant. In other words, even if their consumption is negligible, your body will not experience a deficit in this regard. You can get omega-9 from rapeseed and sunflower oils, almonds and avocados. By the way, olive oil also contains omega acid, but it will be useful for you to know that it is mainly omega-9 and only a small amount of omega-3.
However, despite the fact that omega-9 fatty acids are not required by our body, they have their own health benefits. Thus, recent studies have found that consuming them instead of saturated fats can lower cholesterol levels, as well as the risk of developing diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.