Measurement of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and the use of this indicator as a method of medical diagnosis as early as 1918 was suggested by the Swedish researcher Faro. First, he was able to establish that the ESR indicator in pregnant women is significantly higher than in non-pregnant women, and then he found that an increase in ESR indicates many diseases.
But in the medical protocols of blood tests, this figure entered only a decade later. First Westergren in 1926, and then Winthrop in 1935 developed methods for measuring the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which are widely used in medicine and now.
Laboratory Characteristics of ESR
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate shows the ratio of plasma protein fractions. Due to the fact that the density of erythrocytes is higher than the density of plasma, they slowly sink to the bottom under the influence of gravity in a test tube. Moreover, the rate of this process itself is determined by the degree of aggregation of the red blood cells: the higher the level of adhesion of blood cells, the lower their resistance to friction and the higher the sedimentation rate. As a result, a thick maroon sediment from the erythrocytes appears in the test tube or in the capillary at the bottom, and a translucent liquid remains in the upper part.
Interestingly, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, in addition to the actual red blood cells, is influenced by other chemicals that make up the blood. In particular, globulins, albumin and fibrinogen are able to change the charge of the surface of red blood cells, increasing their tendency to “stick together” with each other, thereby increasing the ESR.
In this case, ESR is a non-specific laboratory indicator by which it is impossible to unambiguously judge the reasons for its change relative to the norm. At the same time, its high sensitivity is appreciated by doctors, who, when changing the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, have a clear signal for further examination of the patient.
ESR is measured in millimeters per hour.
In addition to techniques for measuring the erythrocyte sedimentation rate of Westergren and Winthrop, Panchenkov’s method is also used in modern medicine. Despite some differences in these methods, they show approximately the same results. Consider all three ways to study the ESR in more detail.
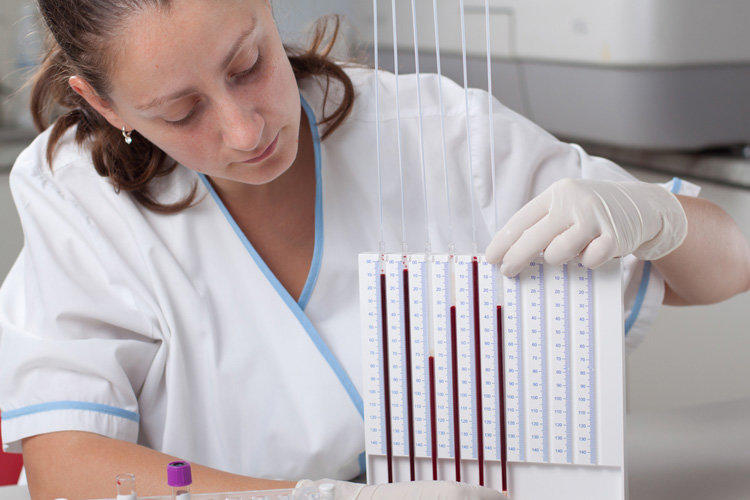
The Westergren method is the most common in the world and it was approved by the International Committee for Standardization of Blood Research. This method involves the collection of venous blood, which for analysis is combined in a ratio of 4 to 1 with sodium citrate. Diluted blood is placed in a capillary, 15 centimeters long with a measuring scale on its walls, and an hour later the distance from the upper border of the erythrocytes to the upper border of the plasma is measured. The results of the ESR study using the Westergren method are considered as objective as possible.
The Winthrop ESR study method is different in that the blood is combined with an anticoagulant (it inhibits the blood’s ability to clot) and placed in a tube with a scale on which the ESR is measured. At the same time, this technique is considered non-indicative for high rates of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (more than 60 mm / h), since in this case the tube is clogged with deposited blood bodies.
According to Panchenkov, the study of ESR is most similar to the methodology of Westergren. The blood diluted with sodium citrate is placed for settling in a capillary with division into 100 units. An hour later, the ESR is measured.
At the same time, the results of the Westergren and Panchenkov methods are identical only in the normal state, and with an increase in the ESR, the first method records higher rates. In modern medicine, with increasing ESR, the Westergren method is considered more accurate. Recently, automatic devices for measuring the ESR indicator have also appeared in modern laboratories, whose work does not actually require human intervention. The functions of the laboratory employee are only to decipher the results.
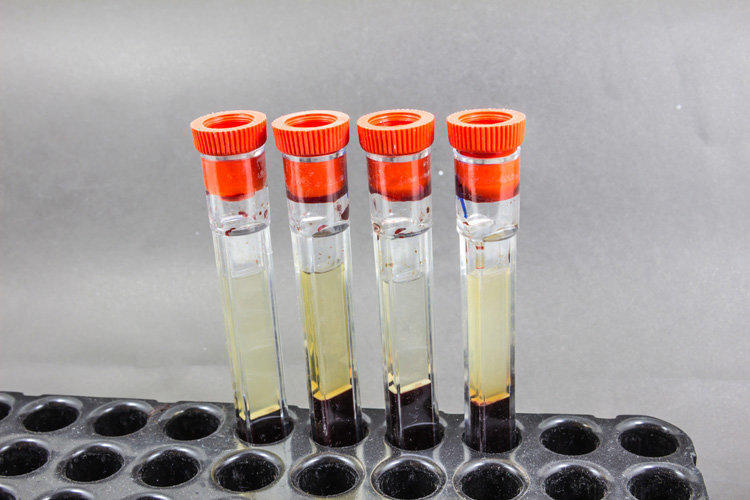
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
The rate of ESR in normal quite seriously differs depending on gender and age of a person. The gradations of this standard for a healthy person are specifically indicated and for clarity, we present them in the form of a table:
| Age Category | Sex | Normal ESR |
| Newborns | boys / girls | 0-2,8 mm / h |
| 1 month | boys / girls | 2-5 mm / h |
| 2-6 months | boys / girls | 4-6 mm / h |
| 6-12 months | boys / girls | 3-10 mm / h |
| 1-5 years | boys / girls | 5-11 mm / h |
| 6-14 years old | boys / girls | 4-12 mm / h |
| 14-18 years old | girls | 2-15 mm / h |
| 14-18 years old | boys | 1-10 mm / h |
| 19-30 years old | women | 8-15 mm / h |
| 31 years old and older | women | up to 25 mm / h |
| 19-60 years | men | 2-10 mm / h |
| 61 years old and older | men | up to 15 mm / h |
In some gradations of the ESR for people aged 60 and over, not a specific indicator is used, but a formula. In this case, in older men, the upper limit of normal is equal to the age divided by two, and in women – to the age plus “10” divided by two. This technique is used quite rarely and only in individual laboratories. The maximum ESR value for it can reach 36-44 mm / h and even higher rates, which is considered by most doctors as a signal of the presence of pathology and the need for medical research.
It is worth noting again the fact that the rate of ESR in a pregnant woman can seriously differ from the above figures. While waiting for a child, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate can reach 40-50 mm / h, which in no way indicates a disease or pathology and is not a prerequisite for any further research.
Causes of ESR Growth
The growth of ESR may indicate dozens of different diseases and abnormalities in the body, so it is always used in conjunction with other laboratory tests. But at the same time in medicine there is a certain list of groups of diseases in which the erythrocyte sedimentation rate invariably increases:
- blood diseases (in particular, in sickle cell anemia, an irregular form of red blood cells provokes an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which differs significantly from the standard indicators);
- heart attacks and strokes (in this case, acute-phase inflammation proteins are adsorbed on surface of blood cells, reducing their electric charge);
- metabolic diseases (diabetes, cystic fibrosis, obesity);
- diseases of the liver and biliary tract;
- tuberculosis ;
- leukemia, lymphoma, myeloma (with myeloma, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate in almost all cases exceeds 90 mm / h and can reach 150 mm / h);
- malignant neoplasms.
In addition, an increase in ESR is observed in most of the inflammatory processes in the body, with anemia and with various infections.
Modern statistics of laboratory studies have collected enough data for the reasons for the growth of ESR, which allowed to create a kind of “rating”. The absolute leader in causing ESR growth is infectious diseases. They account for 40 percent of the detection of excess ESR. Oncological diseases and rheumatism occupied the second and third place of this list with results of 23 and 17 percent. In eight percent of cases of fixation of high erythrocyte sedimentation rate, it was caused by anemia, inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract and small pelvis, diabetes, injuries and diseases of the upper respiratory tract, and a signal of kidney disease in three percent of cases.
Despite the fact that the collected statistics is quite eloquent, it’s not worthwhile to set yourself a diagnosis in terms of ESR. This can only be done by a doctor using several laboratory tests in the complex. The indicator of ESR can very seriously increase, up to 90-100 mm / h, regardless of the type of disease, but in terms of the result of the study, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate cannot serve as a marker of a specific cause.
There are also prerequisites for which the growth of ESR does not reflect the development of any disease. In particular, a sharp increase in the rate is observed in pregnant women, and a slight increase in ESR is possible during allergic reactions and even on the type of food: diet or starvation lead to changes in the blood test and to some extent affect the ESR. In medicine, this group of factors is called the causes of a false positive ESR analysis and they are attempted to be excluded even before the examination.
A separate paragraph is worth mentioning cases where even in-depth studies do not show the reasons for the increase in ESR. Very rarely, the constant overestimation of this indicator may be a feature of the organism, which has neither prerequisites nor consequences. This feature is typical for every twentieth inhabitant of the planet. But even in this case, it is recommended to be examined regularly by a doctor in order not to miss the development of any pathology.
It is also important that in most diseases the growth of ESR does not begin immediately, but after a day, and after recovery, the recovery of this indicator to the norm can last up to four weeks. This fact should be remembered by every physician so that, after completing the course of treatment, he should not subject a person to additional studies due to a residual increase in the ESR.
Causes of ESR growth in a child
The body of children is traditionally different from an adult in terms of the results of laboratory studies. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is not an exception, the growth of which in a child is provoked by a somewhat modified list of prerequisites.
In most cases, increased ESR in the blood of a child indicates the presence of an infectious-inflammatory process in the body. This is often confirmed by other results in the general blood analysis, which together with the ESR almost immediately form a picture of the child’s condition. At the same time, in a small patient, the growth of this indicator is often accompanied by a visual deterioration of the condition: weakness, apathy, lack of appetite — the classic picture of an infectious disease with the presence of an inflammatory process.
Of non-communicable diseases that most often provoke increased ESR in a child, the following should be highlighted:
- bronchial asthma ;
- pulmonary and extrapulmonary forms of tuberculosis;
- anemia and blood disorders;
- metabolic diseases;
- injuries.
However, if an increased ESR is found in a child, the reasons can be quite harmless. In particular, going beyond the normal range of this indicator can be triggered by taking paracetamol – one of the most popular antipyretic drugs, cutting teeth in infants, the presence of worms (helminthiasis), a deficiency of vitamins in the body. All these factors also belong to false positives and they must be taken into account even at the stage of preparation for the laboratory blood test.
Causes of low ESR
Low erythrocyte sedimentation rate relative to the norm is quite rare. In most cases, this situation is triggered by violations of overhydration (water-salt metabolism) in the body. In addition, low ESR may be due to developing muscular dystrophy and liver failure. Among the non-pathological causes of low ESR, corticosteroids, smoking, vegetarianism, prolonged fasting and early pregnancy are distinguished, but there is practically no systematicity in these premises.
Finally, we summarize all the information about the ESR:
- This is a non-specific indicator. Only it is impossible to diagnose the disease;
- ESR growth is not a reason for panic, but is a reason for in-depth analysis. The reasons can be both very harmless and quite serious;
- ESR is one of the few laboratory tests that is based on mechanical action, not chemical reaction;
- The automatic ESR measurement systems that were missing until recently made the laboratory technician’s mistake the most common cause of the false erythrocyte sedimentation rate analysis.
In modern medicine, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate continues to be perhaps the most demanded laboratory blood test. The high sensitivity of the analysis allows physicians to clearly determine the presence of problems in the patient and prescribe further examination. The only serious disadvantage of this study is the strong dependence of the result on the correctness of the laboratory technician’s actions, but with the advent of automatic systems for determining ESR, the human factor can be eliminated.