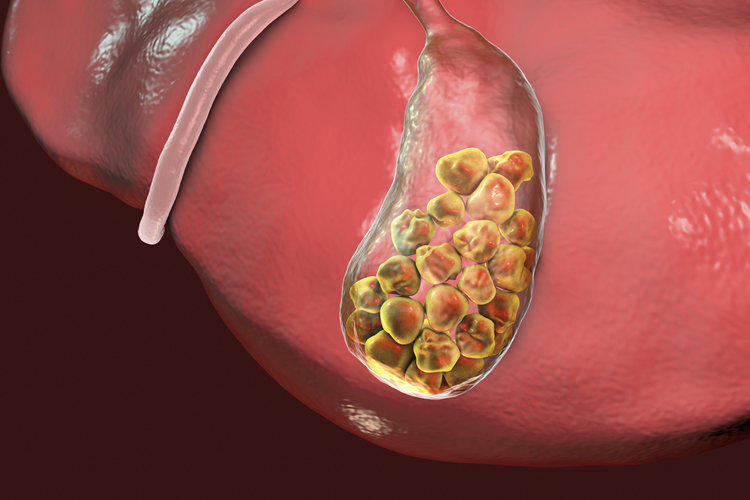
Gallstones are a symptom of gallstone disease, cholelithiasis. Bile contains components that can precipitate, accumulate and form seals – stones in the cavity of the gallbladder or bile ducts. The presence of such inclusions leads to violations of the outflow of bile, inflammatory processes in the membranes of the bladder, infection of the organ and reduces the efficiency of the body’s biliary system.
Why do gallstones form?
Among the factors that provoke the formation of stones in the gallbladder, distinguish leading and additional, concomitant factors:
- the leading factor is considered to be the enhancement of such a characteristic of bile as lithogenicity, which occurs as a result of excessive intake of cholesterol;
- dyskinesia or a decrease in the functional ability of the gallbladder to contract and push the bile into the ducts;
- Bile hypertension in the body due to narrowing of the neck of the gallbladder, which also leads to stagnation of bile;
- localized or common infectious processes that reduce the efficiency of the organs of the hepatobiliary system.
There are various risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing cholylethiasis and the formation of gallstones:
- belonging to the female sex: women suffer from stones formed in the gall bladder, much more often than men;
- elderly and old age;
- gestation period, since increased estrogen levels promote cholesterol secretion to bile;
- irrational diets, fasting, weight loss for various reasons;
- long courses of parenteral nutrition;
- long-term use of drugs containing estrogen, oral contraceptives, sandostatin, ceftriaxone, etc.;
- diabetes;
- some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, hepatobiliary organs, etc.
There are formulas of Tyrek and Faber that allow, by external signs, to suspect a high probability that the patient has gallstones. According to experts, in the group with the highest number of diagnosed stones in bile are women with blond hair and skin, with a history of pregnancy, complete, aged 40 years, with excessive gas formation (flatulence).
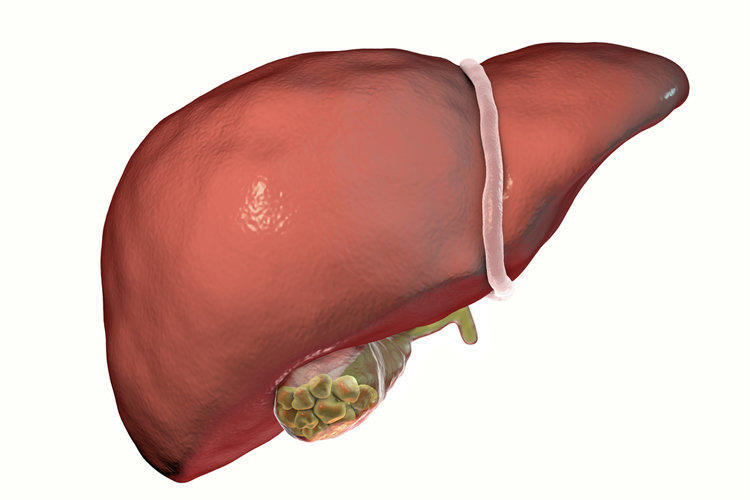
Forms of gallstone disease and symptoms of gallstones
Among the clinical forms of gallstone disease, the following are distinguished:
- latent form or the so-called stone carrier;
- dyspeptic form of the disease;
- pain, accompanied by attacks;
- torpid painful form;
- cancerous.
A significant number of patients with cholelithiasis (60-80%) have no symptoms or manifestations of the disease in the presence of gallstones. However, this period represents the latent form of the disease rather than the static one. According to the observations, up to 50% of patients within 10 years after the discovery of stones in the gallbladder consult a doctor about the occurrence of symptoms indicating the development of other forms of gallstone disease and its complications.
The dyspeptic form is clinically expressed in disorders of the functioning of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Most often this is reflected in the appearance after eating a feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region, increased gas formation, bloating, heartburn, and bitter mouth. This form is often combined with painful paroxysmal, or manifestations of biliary colic, since palpation can detect pain in characteristic points.
The painful paroxysmal form is manifested in biliary colic and is the most common variant of the clinical form of cholelithiasis, diagnosed in 75% of patients. The disease manifests itself in the form of sudden, recurring attacks of pain in the right hypochondrium with possible irradiation to the back or to the right scapula. The attack may be accompanied by nausea, reflex vomiting, not bringing relief. If the duration of the attack is more than 6 hours, acute cholecystitis is diagnosed.
The torpid form of gallstone disease is accompanied by constant dull pain in the area of projection of the gallbladder without periods of remission and no pain.
In about 3% of cases, cholelithiasis is accompanied by the development of tumor formations. According to various data, from 80 to 100% of cancer patients with cancer in the gallbladder have stones in the organ cavity. Presumably tumors arise as a result of changes in the chemical composition of bile with cholelithiasis, prolonged irritation and traumatization of the inner membranes of the bladder with gallstones, the addition of infection.
Among the common symptoms common to most patients with stones in the gall bladder, the following signs of the disease can be identified:
- pain or discomfort during palpation in the right hypochondrium, feeling of heaviness in the epigastric region, associated with taking spicy, fatty, fried foods or alcohol;
- change stool color, discoloration;
- intestinal dysfunction: constipation, unstable, irregular stools, flatulence, etc.
- complaints of heartburn, bitter taste in the mouth, etc.
GCB therapy: how to treat gallstones?
Complicated forms of gallstone disease and prevention of their complications are subject to treatment. In the presence of stones without a clinical picture of cholecystitis, therapy consists of following a diet, regimen, maintaining an active lifestyle to reduce the likelihood of bile stagnation and related complications, and taking medications that destroy the structure of stones (Henofalk, Ursosan, and others). With single inclusions of stones, stones and the absence of signs of disease in modern medicine using the method of shock-wave therapy.
Food should be frequent, fractional, with small portions of food. Fatty, spicy, fried foods and alcohol are excluded from the menu. It is necessary to monitor the amount of cholesterol in the consumed dishes and include food rich in fiber (cereals, herbs, vegetables) in the diet.
Conservative treatment during acute attacks can be both a method of therapy and a type of preoperative preparation in patients with destructive cholecystitis. In conservative therapy include several procedures and techniques, which are based on the well-known formula “cold, hunger and peace”:
- full hunger for vomiting, if the attack is not accompanied by vomiting, you can drink water;
- cold (ice) on the right hypochondrium, local hypothermia method to reduce inflammation and hypertension of the gallbladder;
- antibacterial drugs in the inflammatory process;
- detoxification therapy and forcing the output of fluid from the body with diuretic drugs;
- relief of painful attacks with the help of analgesics (Maksigan, Analgin) and antispasmodic drugs (Papaverine, No-Spa, Baralgin, Platyphylline, etc.) or combination medications with anesthetic and antispasmodic action.
How to treat gallstones in additional ways? In addition to targeted actions and drugs, ancillary therapy is prescribed: drugs that stimulate the secretion of bile acids, enzymes for the digestive system, including destructive fats, drugs to restore balance in the composition of bile, as well as the lithotripsy method, both shock wave and drug therapy, and Litolysis method for crushing or dissolving stone stones. Crushed stones are able to go out independently with feces.
Surgical treatment as a method of therapy is prescribed for frequent attacks of acute cholecystitis, a large amount of stones, a destructive course of the disease and the presence of serious complications. The method of surgical treatment can be based on open or laparoscopic penetration and various types of manipulations with the gallbladder.
Therapy is carried out exclusively under the supervision of doctors, as independent attempts to take drugs for crushing and the removal of calculus can lead to blockage of the bile ducts, obstructive jaundice, acute holicestitis and other complications of the disease.
The most common surgical method of treatment is used in patients with acute intractable other types of cholecystitis treatment in a condition that threatens the patient’s life. In acute form of destructive cholecystitis, the operation is performed in the first 24-48 hours after hospitalization. The choice of surgery (cholicysectomy, gallbladder removal, or decompression with the withdrawal of infected bile) depends on the nature of the inflammatory process and the disease, and on the physical condition of the patient.