Salmonellosis is an infectious disease that primarily affects the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. The causative agent of salmonellosis are bacteria of the genus Salmonella. Salmonellosis is characterized by a severe course, and the risk of contracting the disease is large enough, so anyone should know how the disease manifests itself and how to avoid it.
Salmonellosis – what is it?
Salmonellosis refers primarily to a zoonotic disease. So called diseases transmitted to humans from animals or from products derived from animals. Thus, the source of infection can be as live animals (dogs, cats, cows, pigs, wild and domestic birds, fish), and animal products – meat, milk, eggs.
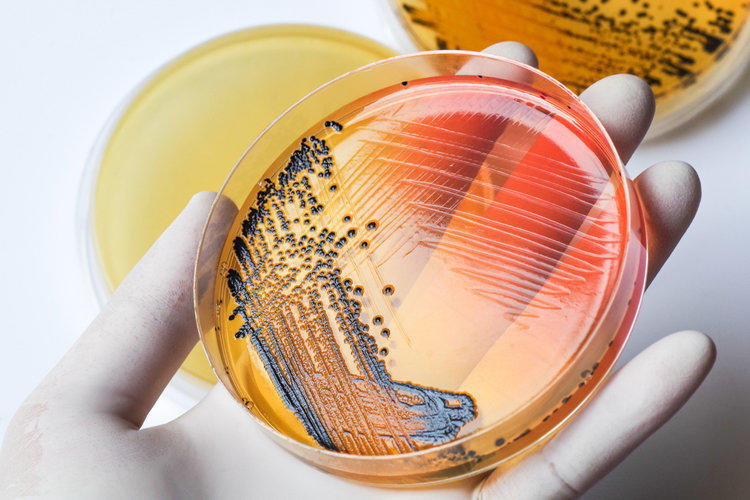
Bacteria of the genus Salmonella are Gram-negative. They are highly resistant to adverse effects. Bacteria can live for weeks or months in water, on surfaces of objects, in meat and milk of animals at room temperature. They can also withstand a significant (up to -80 ° C) lowering of temperature. Boiling and heating up to + 100 ° C quickly kills microorganisms, but they can live for several tens of minutes in water with a temperature of up to + 70 ° C.

Neither salting nor preservation does not kill these bacteria. Their only “Achilles heel” – the impact of disinfectants – most of them quickly kill salmonellosis bacilli. Also, salmonellosis bacteria are highly resistant to most antibiotics.
The mechanism of the development of the disease
Infection usually occurs after contact with infected animals, after eating food containing salmonella. It is also possible infection by airborne droplets, through the water, everyday objects. The source of infection may be other people who are carriers of salmonellosis bacilli.
It is not every time when a bacteria enters the body through the mouth disease occurs. First, the bacteria enter the human stomach, containing gastric juice. Salmonella is sensitive to an acidic environment, so gastric juice, containing hydrochloric acid, can kill some bacteria. Therefore, people with problems with the secretion of gastric juice have the highest sensitivity to bacteria.
If the gastric barrier was successfully passed, the bacteria colonize the intestines and begin their destructive activity. They can attach well to the intestinal mucosa and penetrate into the superficial tissue. In this case, bacteria can secrete various toxins that poison the body and cause malaise, vomiting and diarrhea. Dying salmonellae also release dangerous toxins.
Salmonella is also very good at circumventing the body’s defenses. Having discovered an invasion, the immune system sends special cells, macrophages, to meet the causative agents of the disease. However, Salmonella have learned to use these cells to their advantage. Being absorbed by macrophages, some salmonellae do not die, but move with them along the bloodstream and thus move to other tissues of the body. Thus, Salmonella can affect not only the intestines, but also the liver, kidneys, heart, and even the meninges. This feature of the pathogens of salmonellosis is the reason that the disease can lead to serious complications and go far beyond the gastrointestinal tract.
Salmonellosis can make anyone sick, regardless of age or gender. However, young children and the elderly are most susceptible to it because of their weakened immunity. In addition, they have the disease is more severe.
The disease has a pronounced seasonal dependence. In the warm season there is a peak of disease. However, salmonella infection can occur in any season.
Symptoms of salmonellosis
There are two main options for the disease – gastrointestinal and generalized. The second, in turn, is divided into typhoid and septic. The gastrointestinal tract is the lightest, and the septic version is the most severe, with the highest probability of death.
Gastrointestinal Form
Typical symptoms in this form of the disease:
- High temperature,
- Liquid stools with characteristic discharge,
- Abdominal pain,
- Nausea,
- Vomiting.
This form does not generally extend beyond the gastrointestinal tract. The incubation period of the disease is small. It usually ranges from 3 to 72 hours. After that, the patient has a fever and begins to have stool disorders, nausea and vomiting.
Characterized by acute pain in the abdomen, most often in the upper part, near the navel. The symptoms of salmonellosis also include a very high temperature, which can rise up to + 40 ºС. Stools frequent – up to 10 times per day and can lead to dehydration. The stool usually has a watery and frothy texture, contains green mucous clots and has an unpleasant odor. Spotting may appear a little later, on the third day.
In addition, the patient may experience a drop in pressure, tachycardia, and a change in heart sounds. This form usually lasts no more than a week.
The gastritic form is a type of gastrointestinal form. Usually, the disease with it is easier, diarrhea is not observed, only vomiting, painful sensations are localized in the epigastric region. This form is quite rare.
Typhoid form
In typhoid salmonellosis, the symptoms at first resemble the symptoms of the gastrointestinal form – vomiting, diarrhea, high fever. However, then the disease takes on features that make it similar to typhus. A rash appears on the skin; many organs increase in size – spleen, liver. This form has a more severe course and lasts longer – in some cases more than a month.
Septic form
In most cases, it is typical for persons with weakened immunity, the elderly, young children. In the septic form of salmonellosis, symptoms are not limited to fever and signs of general intoxication. It is also characterized by infectious processes in various organs, primarily in the lungs, kidneys, and bladder. Damage to the endocardium and meninges may be observed.
For septic salmonellosis, life-threatening complications such as pulmonary and brain edema, renal and heart failure are more common. With this form of salmonellosis, treatment is extremely complicated.

Diagnostics
Not all symptoms, including diarrhea and fever, mean that it is salmonellosis. Salmonellosis, especially at an early stage, is not always easy to separate from other infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as rotavirus infection, dysentery. Therefore, to determine the causative agent, patient feces analysis is necessary. In generalized forms of pathogens can be detected in the blood. Also an important role in the diagnosis is played by the analysis of actions that could lead to infection.
How to treat salmonellosis
How to treat a disease, only a doctor can decide. In most cases of salmonellosis, treatment is carried out in a hospital. In the case of milder forms of the disease, treatment can also be carried out at home. However, this is more likely an exception, since salmonellosis is an insidious disease, and its seemingly mild course at any time can be replaced by an exacerbation.
For mild salmonellosis, treatment is mostly symptomatic. If a person has gastrointestinal salmonellosis, then the main attention is paid to the rehydration of the body, that is, the restoration of the lost fluid. Water-salt solutions are used for this purpose. Also, in the first days of the disease, gastric and intestinal lavages are regularly made, sorbents are used, which absorb bacteria and their toxins, and they carry out deintoxication therapy with the help of colloidal solutions. Enzyme preparations are used to restore digestive functions (pancreatin, dry bile).
In addition, the need to take drugs – probiotics, restoring the normal intestinal microflora.
A patient should drink as much liquid as possible. A hungry diet is not shown, instead it should use a sparing diet – boiled dishes, low-fat soups, cereals. Antidiarrheal drugs such as Loperamide are not recommended, as they slow down the elimination of toxins from the body and can lead to severe intoxication.
Antibiotics for mild salmonellosis are rarely used. This is due to the fact that Salmonella has a high resistance to most antibacterial drugs and the fact that antibiotics can exacerbate intoxication. However, in severe salmonellosis, treatment may include antibiotics. Also, antibiotics are used in cases where other forms of therapy demonstrate low efficacy. Most often, fluoroquinolones are used in the treatment of salmonellosis, but only a doctor can prescribe a specific type of antibiotic. There are also special preparations containing bacteriophage viruses active against Salmonella.
Vaccination for salmonellosis is not done. This is due to the fact that the varieties of bacteria that can cause salmonellosis, a great many – a few hundred, and the universal vaccine in this case can not be developed. In addition, immunity to salmonellosis in humans is usually unstable and goes away after about a year.
After recovery, there should be a recovery period, which can take several months. This will help avoid the negative effects of salmonellosis.
Recovered patients, however, can carry Salmonella in the body for a long time and can be dangerous to others because of the possibility of infecting them. The effects of salmonellosis also include dysbacteriosis, which is to be treated with probiotic preparations.
Prevention
Prevention of the disease is in principle similar to the prevention of other infections of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, but it has some peculiarities. They are related to the fact that the main source of infection is animals and poorly processed products obtained from animals. Thus, in order to protect yourself from salmonella disease, you must follow simple rules – do not eat raw, poorly roasted or boiled meat, fish or eggs. It should be remembered that salmonella does not die even after prolonged cooking, within a few hours, if the meat is more than 15 cm thick. Thus, before cooking the meat, poultry and fish, they should be cut into smaller pieces.
Special attention should be paid to the eggs. Poultry is most often the bearer of salmonella. Therefore, you should abandon the use of raw eggs and cook them as long as possible – at least 6 minutes. It is also necessary to pay attention to the surface of the eggs themselves, since they may be particles of bird droppings. Therefore, after the eggs were taken with your hands, you should wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
However, there is an exception – quail eggs are extremely rarely affected by salmonella, so you can even eat them raw. However, they must also be washed before use.
You should also pay attention to the procedure for cutting raw meat. Some housewives can use the same knife and cutting board for cutting raw meat, poultry and fish and slicing raw foods. This should not be done – for these purposes you should use a variety of devices. Meat boards and knives are best washed after use. Also, do not eat raw milk – only boiled or pasteurized.
However, salmonella can also live in products that seem to have nothing to do with animals, such as confectionery. This is explained by the fact that infected eggs could be used to make flour in such products. Therefore, in general, it should be the rule not to buy questionable food from the hands of street vendors.
Other salmonellosis prevention tips are consistent with standard hygiene rules – wash your hands regularly, especially after visiting the street, contacting animals, not drinking unboiled water, etc. And, of course, strengthen the immune system, treat chronic diseases that can lead to the body’s vulnerability to infection.