- Description of the drug chlorhexidine
- Indications for chlorhexidine
- Side Effects
- Interaction with other substances
- Dosage Forms
- Instructions for use of chlorhexidine
- Treatment of diseases of the oral cavity and throat
- Venereal diseases and gynecology
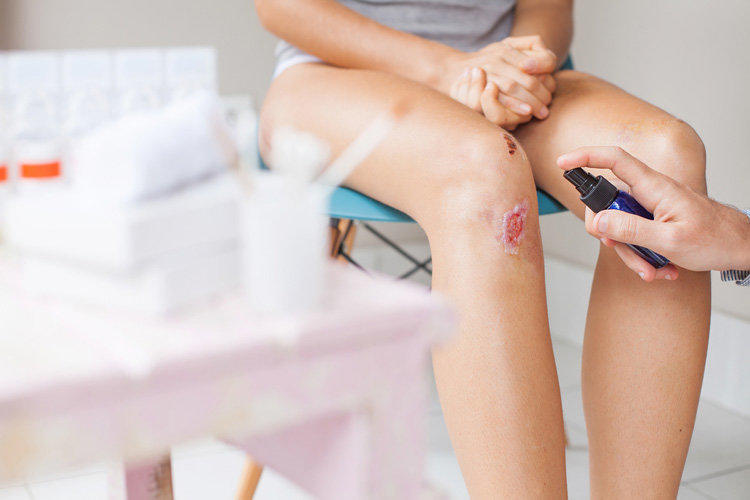
- Disinfecting wounds, skin surface
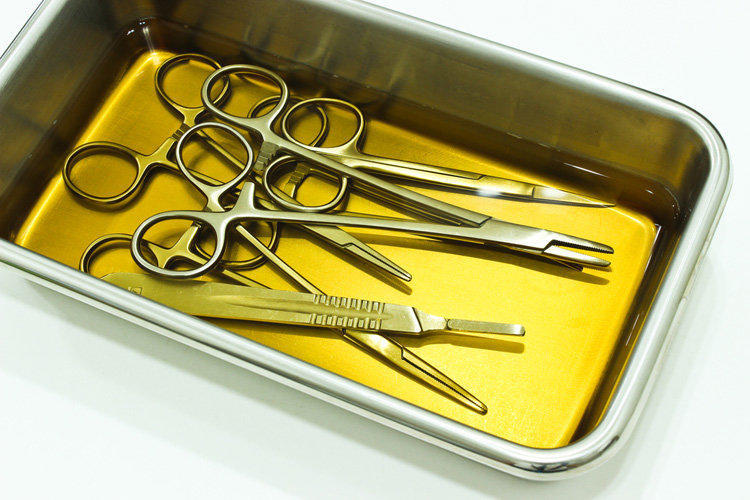
- Disinfecting medical staff and medical devices
- Chlorhexidine Ointment
Many of us can find various antiseptics in our first aid kit. In general, it is iodine, brilliant green, potassium permanganate. Recently, these drugs began to be displaced by chlorhexidine. What is this drug, and is it justified to use instead of well-proven antiseptics?
Description of the drug chlorhexidine
The drug was discovered in the UK in the early 1950s. However, data on its high performance and safety did not appear immediately. At the beginning the drug was treated with caution, because it was not known what side effects it may cause. And only after they were not found, chlorhexidine began its widespread use.
Chlorhexidine is a universal broad-spectrum bactericidal agent. There are few bacteria that resist it. In addition, the drug is active against many fungi and even against some viruses, for example, the herpes virus.
From a chemical point of view, the drug refers to chlorinated derivatives of biguanide. In the finished dosage forms chlorhexidine is contained in the form of digluconate. The principle of the drug is based on its interaction with the membranes of bacterial cells. Chlorhexidine reacts with phosphate groups on the surface of membranes, which leads to osmotic imbalance and subsequent destruction of the membrane, as a result of which microorganisms die. Those fungi and viruses that, like bacteria, have lipid membranes, can also be exposed to the drug. Although in this respect, the drug is still inferior to antifungal and antiviral drugs.
The drug is active against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It is characteristic that the bacteria have so far failed to develop resistance to the agent. Chlorhexidine is weakly active only to some strains of pseudomonads, bacteria of the genus Proteus, bacterial spores. The fungal spores are resistant to chlorhexidine. Slightly affects the drug and the livelihoods of lactobacilli.
The activity of the drug increases with increasing temperature. However, when reaching +100 ºC, the drug begins to partially decompose. The advantage of chlohexidine over other antiseptics is its high activity in the presence of pus. Not every antiseptic can boast of this. True, pus and blood reduce the activity of the drug, but only slightly. In addition, the drug retains activity for a long time. When applied topically, the substance does not enter the systemic circulation.
The price of the drug is low, it is sold without a prescription.
Indications for chlorhexidine

The scope of the drug is diverse. This is the processing and treatment of wounds, cuts, acne, acne, prevention and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases. The drug is widely used to treat diseases of the oral cavity – stomatitis, periodontitis, gingivitis, upper respiratory tract – pharyngitis and tonsillitis, for the treatment of dentures.
Also, the drug is often used to disinfect the hands of the surgeon, surgical instruments, the surgical field during operations and other medical procedures, disinfection of medical equipment, thermometers, etc. In addition, the drug is necessary for disinfecting the hands of employees of public catering enterprises, the food industry and public utilities.
The drug has a high degree of safety. It can be used in childhood and during pregnancy. However, since the drug is used relatively recently compared with most other antiseptics, caution is recommended.
Side Effects
An important feature of the drug is its relatively low toxicity. It almost does not affect the cells of the human body. However, this, of course, does not mean that the drug is completely harmless.
Taking it inside is still not recommended. If this happens, then you should use sorbents, such as activated carbon and make a gastric lavage. In addition, it can cause burns of mucous membranes. For this reason, chlorhexidine cannot be used for the treatment of infectious inflammation of the eye, such as conjunctivitis . In case of contact with eyes, rinse thoroughly with water.
You should also avoid getting the drug on the meninges, for example during open head injuries. It is forbidden to use the drug for the treatment of ear diseases in case of damaged eardrum.

It is not recommended to use the drug as a means for permanent prevention of skin diseases, since this can lead to the death of not only harmful microorganisms, but also beneficial bacteria that live on the skin. Occasionally, allergic reactions to the drug can occur – skin rash, dermatitis.
When using the preparation as a means for rinsing, taste sensations may change. The appearance of tartar and discoloration of teeth is possible.
Interaction with other substances
Chlorhexidine generally interacts favorably with other substances. However, there are a few exceptions. Simultaneous use together with iodine can lead to the occurrence of dermatitis. It is not recommended to use the drug in conjunction with soap and other anionic alkaline substances, since this significantly reduces its effectiveness. In this case, chlorhexidine can be combined with cationic substances, such as alconium benzoate. Ethyl alcohol increases the activity of the drug. For this reason, alcohol solutions are very popular.
Dosage Forms
There are several dosage forms of the drug. The main one is an aqueous solution. It can be of different concentrations – 0.01%, 0.05%. 0.2%, 0.5%, 1%, 2%, 5%.
In everyday life, the most commonly used solution is 0.05%. It is sold in small polymer or glass bottles. Solutions with a high concentration are most often used for disinfecting medical equipment and medical personnel’s hands, treating medical instruments, and also for preparing solutions of lower concentration from them.
There are also other dosage forms:
- Sprays
- Ointments
- Creams
- Gels
- Alcohol solutions
- Vaginal suppositories
Instructions for use of chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine is very simple. However, it must be remembered that solutions of different concentrations are required for the treatment of various diseases.
Treatment of diseases of the oral cavity and throat
For sore throat, pharyngitis and tonsillitis, a solution from 0.2% to 0.5% is suitable. Before rinsing the throat with chlorhexidine, rinse the throat with warm water.
For rinsing, take a tablespoon of solution (10-15 ml). The duration of the procedure is approximately 30 seconds. After rinsing, it is advisable not to eat or drink anything for an hour. If you feel a burning sensation while rinsing your mouth, then the concentration of the solution is too high, and you should take a less concentrated solution.
It is not recommended to use the solution for the treatment of the nasopharynx for sinus, as the drug may get into the inner ear. If necessary, you should consult your doctor, who will tell you how to use the drug.
In dentistry, you can use the mouthwash after tooth extraction. Rinse is carried out three times a day for 1 minute.
When processing the oral cavity, remember that you should not swallow the drug, especially in high concentration (0.5%). If this happens, you should take activated carbon.
Venereal diseases and gynecology
The most effective chlorhexidine in the prevention and treatment of sexually transmitted diseases, including gonorrhea, syphilis, trichomoniasis, chlamydia. In particular, in the case of unprotected sexual intercourse, men should inject 2-3 ml of drug into the urinary canal. Women are required to inject 1-2 ml into the urethra and 5-10 ml into the vagina. After treatment with the drug should refrain from urinating for about 2 hours. In addition, it is recommended to treat the surface of the skin around the genitals with the drug.
Chlorhexidine is also often used in gynecology. For gynecological diseases such as vaginitis and vulvovaginitis, vaginal suppositories can be used. They can be used in childhood. Chlorhexidine is also used in the treatment of thrush. For this, douching with a solution of 0.05% is used.
Disinfecting wounds, skin surface
In dermatology, the drug is used to treat mucous membranes affected by bacteria that are sensitive to its effects. When disinfecting wounds and burns, a small amount of the preparation – 5-10 ml should be applied to the treated surface. It should be at the same time to take solutions from 0.05% to 0.5%. Application time is 1-3 minutes. You can also use a spray for this purpose.
Disinfecting medical staff and medical devices
When treating the hands of medical staff, take 5 ml of the solution. This amount is rubbed into the skin for about 2 minutes. When processing the operative field or elbow bends, when taking blood, the surface is twice wiped with an abundantly moistened swab in the product. Hold time – 2 minutes.
For disinfection of the skin before surgery, an alcohol solution of chlorhexidine is used. For its preparation is taken 1 part of a 20% solution of the drug and 40 parts of 70% alcohol. Medical instruments are treated with a 0.5% solution heated to 70 ºС.
Chlorhexidine Ointment
Also, ointments and creams containing chlorhexidine are used to disinfect hands and skin. After applying to the skin, the ointment begins to act within 15 seconds. A thin layer of substance is formed on the skin, preventing the penetration of microbes. The bactericidal action of the ointment lasts for several hours.