Intestinal flu – the everyday name of the disease, which, in fact, is not the flu. Many have probably come across this disease. His symptoms are indeed somewhat similar to flu symptoms – malaise, fever and other signs of intoxication. But instead of the respiratory tract, intestinal flu affects the gastrointestinal tract. This is expressed in various disorders of the stomach and intestines – diarrhea, changes in the appearance of feces, nausea and vomiting.
Description of the disease
However, the usual flu and intestinal flu still have some similarities. This is what both diseases are viral. Regular flu is caused by a flu virus, and intestinal flu is caused by a virus belonging to the rotavirus family. Thus, influenza and intestinal flu are caused by various pathogens, so these diseases have a slightly different nature.
Often, intestinal flu includes gastrointestinal diseases caused not only by rotaviruses, but also by Norfolk viruses and adenoviruses. However, these diseases are not so common, so most often under the intestinal flu means a disease caused by rotavirus. Viral gastrointestinal pathologies are also often combined together under the name “viral gastroenteritis”.
Rotavirus was discovered relatively recently, in the 70s of the 20th century. Prior to its discovery, rotavirus gastroenteritis was not isolated in a separate disease, and it was believed that it is caused by various pathogenic bacteria. However, after the discovery of rotavirus, it became clear why many gastroenteritis, especially in children, are difficult to treat with antibacterial agents.
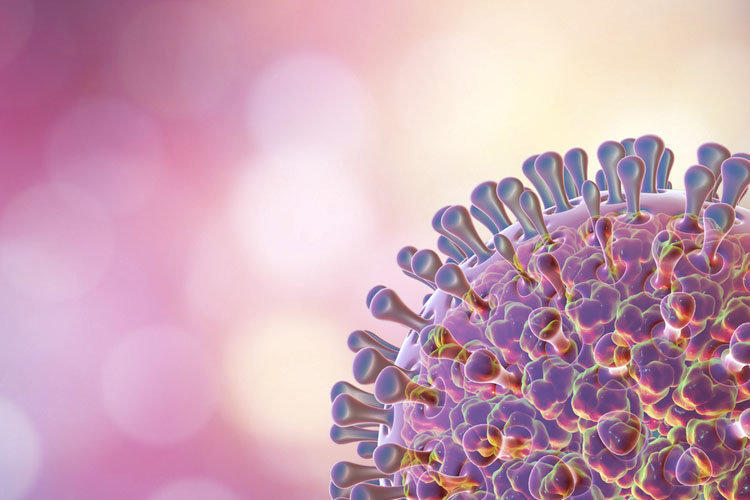
If you can apply aesthetic measures to the world of microorganisms, then rotavirus, perhaps, can be attributed to the most beautiful. It has an almost perfectly round shape and is “stuck” on all sides with peculiar protruding spikes formed from protein molecules. It is for this form that rotavirus got its name from the Latin word “company” – the wheel.
However, behind the attractive appearance of the rotavirus hides a very aggressive and cruel essence. In the world every year tens of millions of rotavirus infections are recorded. And the mortality from it, alas, is quite high. In just one year, rotaviruses kill nearly a million people. And more than half of them are children under 5 years old. Thus, the mortality from intestinal flu exceeds the mortality from the usual and is somewhere around 2%.
That is why it is important to know what constitutes intestinal flu, the symptoms and treatment of the disease, its prevention. In Russia, intestinal flu epidemics occur in the autumn-winter period and roughly coincide with the spread of ordinary flu epidemics.
Most cases are children under 5 years old. In general, intestinal flu is primarily a childhood disease. Of course, the disease of intestinal influenza in adults is also not uncommon. However, they usually have a disease that is not so pronounced or passes faster. Often, infection with intestinal flu in adults is perceived as a banal stomach upset or food poisoning. This is largely due to the fact that in adults the immunity is stronger than in children. In addition, children have less acidic gastric juice than adults, which means that children are more likely to get viruses through the stomach and settle in the intestines.
By the way, for infection with rotavirus infection, an insignificant number of viruses are needed – no more than 100. The incubation period for the development of the disease is 5 days. And the whole disease can last up to two weeks. The favorite habitat of the virus is the villi of the epithelium lining the surface of the small intestine. Rotavirus can also live in the duodenum.
In addition to rotavirus, which causes the common intestinal flu, which most children have, there are other types of rotavirus. In particular, rotavirus B, which causes a disease called “adult rotavirus infection.” This disease, however, is more common in Asian countries. There are also rotaviruses that cause similar diseases in various animal species.
Symptoms of the disease
Intestinal flu can often begin as a cold, with a little sore and sore throat. However, respiratory symptoms soon disappear and give way to symptoms of gastric disorder. These signs can accurately recognize the intestinal flu. Gastrointestinal disorder symptoms include nausea, diarrhea (stools up to several times a day), pain in the lower abdomen and the epigastric region, and sometimes vomiting. Also, the disease is accompanied by a significant increase in temperature, which sharply distinguishes it against the background of other infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. The temperature can reach + 38-39 ºС.
Against the background of high fever and diarrhea, signs of exhaustion and dehydration develop:
- weakness
- pallor,
- respiratory impairment,
- cardiac abnormalities.
Loss of fluid is a very dangerous symptom, it is the one that is fatal in most cases of the disease.
Diagnostics
When diagnosing, it is important to separate viral gastroenteritis from bacterial, because the treatment of these diseases is very different. It is also important not to confuse rotavirus infection with food poisoning. However, this is not difficult to do, since there is usually no increase in temperature in food poisoning. To identify the pathogen can be carried out various analyzes, such as PCR analysis.
Treatment
Treatment of intestinal flu in adults and children is predominantly symptomatic. To date, there are no antiviral drugs that act directly against rotaviruses. Symptomatic treatment has two main areas – relieving symptoms of inflammation and helping the body to restore the required amount of fluid.
Antipyretics for intestinal flu are taken only if the temperature exceeds +39 ºС, or the patient does not tolerate the temperature. This is due to the fact that hyperthermia is one of the main means of combating the body against infection. The higher the body temperature, the more viruses die. Therefore, lowering the temperature, we interfere with recovery.
For intestinal flu, treatment should also be aimed at replenishing water loss by the body. In order to prevent this, you should give the patient more drink, especially warm. It can be fruit drinks, teas, jelly, juices. Drinking milk drinks for intestinal flu is not recommended.
In case of a strong degree of dehydration, you can use rehydration solutions or give the patient to drink salted water.
Use antibiotics for intestinal flu are not only meaningless, since they do not act on the pathogen, but are often harmful, since antibacterial drugs can destroy the remains of beneficial intestinal microflora. Only in the case when rotavirus infection is combined with a bacterial infection, antibiotics can be used. However, they can be taken only as prescribed by a doctor and nothing else.
Since the disease affects the beneficial intestinal microflora, it is necessary to take probiotic preparations to restore it, for example, Linex and Bifidumbakterin. Sorbents are used to absorb viral particles and their toxins – Smecta, activated carbon.
Great importance in the treatment of rotavirus infection is diet. The patient must take boiled and easily digestible food. You can not roast, salty, sweet, dairy products.
Etiotropic, that is, directed against the pathogen itself, therapy does not exist. However, rotavirus vaccines have been used successfully in many western countries. In some countries, vaccination of children is even mandatory. In addition to vaccines, drugs can also be used to stimulate the immune system.
Those who have had a rotavirus infection still have strong immunity to the disease. With subsequent infection with the virus, the intestinal flu either does not appear at all or is mild. However, there are many strains of rotavirus, and if a person is immune to one, then nothing prevents him from becoming infected with another, to which he has no immunity.
Prevention
Therefore, we must not forget about the prevention of the disease. It includes standard measures for maintaining personal hygiene – washing hands, especially after visiting the street, crowded places and toilets, washing food, especially fruit and vegetables, heat treating food if necessary, boiling drinking water, regular wet cleaning of the room. Adults who have children in the family should pay special attention to personal hygiene, since many adults can be distributors of rotaviruses themselves, without becoming ill and unaware of their virus carrier.