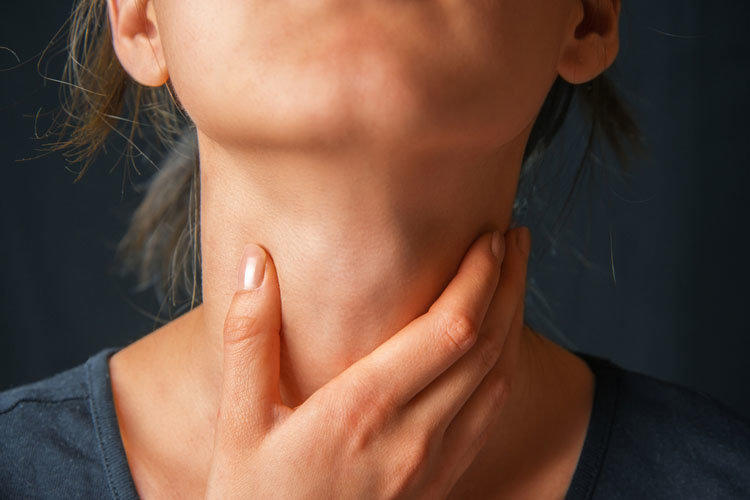
Chronic tonsillitis is a disease of the upper respiratory tract, characterized by a long inflammatory process of the tonsils. The cause of the development of chronic tonsillitis most often becomes an ineffective or incomplete course of treatment of acute tonsillitis. A prolonged decrease in local immunity leads to the formation of foci of inflammation of the glands, in which pathogens are activated at the onset of exacerbation of the disease.
Prevalence and Danger of Illness
The prevalence of chronic tonsillitis is quite high: according to some data, up to 10% of the population of European countries are subject to the disease. The disease can affect both adults and children. In addition to the discomfort experienced by a patient with chronic tonsillitis, this infectious disease is dangerous by the presence of a permanent focus of inflammation and infection in the body, which leads to such complications of tonsillitis as rheumatism, pyelonephritis, rheumatic heart disease, polyarthritis, the development of autoimmune diseases and so on. That is why anyone should know everything about chronic tonsillitis, treatment and symptoms of this disease.
Causes of chronic tonsillitis
Palatine tonsils (in common parlance – the glands), consisting of lymphoid tissue, are part of the overall immune system of the body. Their main purpose is the fight against infectious agents penetrating the human throat. Normally, the human microflora consists of non-pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microorganisms that are in a state of natural balance due to the combined work of all the organs of the immune system. In case of imbalance, penetration of pathogenic organisms, stress of local immunity leads to the destruction of viruses, fungi and bacteria. With frequent stress immunity, a large number of pathogenic flora, a general decrease in body resistance, lymphoid tissues become unable to produce enough interferons, lymphocytes, gamma globulins to resist infectious agents.
With frequent and / or prolonged inflammatory processes in the pharynx, the tonsils lose the ability to express resistance to pathogenic organisms, tissue cleansing and themselves become a source of infection, which leads to the development of chronic tonsillitis. Usually the tonsils become inflamed due to the presence of lacunae in them. Gland lacunae are reservoirs for the accumulation of epithelial cells and various microorganisms. According to the analysis of microflora, about 30 different pathogenic microorganisms are isolated on the surface of tonsils in patients with tonsillitis, bacterial analysis of the lacunae content most often reveals a high concentration of streptococci and staphylococci.
Most often, the chronic form of the disease develops after an acute inflammatory process, tonsillitis. Occasionally, in 3 cases out of 100, a focus of chronic inflammation is formed without an acute form in immediate retrospect. The following pathologies and diseases of bacterial and viral etiology contribute to the development of the chronic form of the disease:
- purulent sinusitis, antritis, adenoiditis, as well as any inflammatory processes and pathologies of the structure of the nasal passages that violate nasal breathing;
- caries, gingivitis and other foci of concentration of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity;
- a short history of measles, scarlet fever, the current tuberculous process, and other infections that reduce overall immunity, especially in latent, severe forms or improper treatment of diseases.
There are also the role of a hereditary susceptibility to tonsillitis of the chronic form and a number of factors contributing to a decrease in local immunity in the nasopharynx:
- insufficient, uniform in composition diet, lack of vitamins, minerals;
- insufficient fluid intake, poor water quality;
- severe and / or prolonged hypothermia of the body, frequent sudden drops in ambient temperatures;
- severe and / or prolonged psycho-emotional overstrain, mental exhaustion, depressive states;
- adverse living conditions, labor, gas pollution, exceeding the permissible concentration of harmful substances;
- bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse.
If there is a chronic focus of inflammation, the lymphoid tissue is replaced by connective tissue, scar formation, narrowing of the external opening of the lacunae, which causes the formation of lacunary and purulent traffic jams, purulent raids. All this enhances the general inflammation of the organ. Lacunar aggregations of pathogenic microorganisms, food particles, purulent secretions lead to the penetration into the bloodstream and the spread of bacteria, toxins secreted by them and products of destruction throughout the body, causing chronic intoxication. Sensitivity of tissues and organs to irritants and foreign proteins increases, allergic, autoimmune processes and severe complications of tonsillitis occur.
Types, symptoms of chronic tonsillitis and complications of the disease
When making a diagnosis, local and systemic symptoms are assessed, anamnesis is taken, an analysis of the patient’s complaints and the overall clinical picture of tonsillar syndrome are carried out. Local tonsillitis symptoms that are important in the diagnosis are manifestations of any inflammatory processes in the tissues of the tonsils. In chronic form, the symptoms characteristic of the whole organism (systemic) are explained by the effect of cytokines and tissue breakdown products that spread from the infectious focus with the bloodstream. You should also consider the effect of toxic substances secreted due to severe microbial invasion of the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils. Depending on the nature, frequency of exacerbations and the general reaction of the body, several types of chronic tonsillitis are distinguished:
- Simple recurrent chronic tonsillitis, with frequent acute tonsillitis.
- A simple prolonged tonsillitis, with signs of a constant, sluggish inflammatory process.
- Simple compensated, with long periods of remission and rare relapses.
- Toxic-allergic tonsillitis.
The toxic-allergic form of the disease includes two varieties. In the first variety, a number of symptoms are observed, indicating an increase in the level of allergization and intoxication of the organism. These are hyperthermia, pain in the region of the heart, fatigue, pain in the joints. Signs are not accompanied by functional disorders of organs and systems.
At the second stage, signs of intoxication are confirmed by examinations: cardiac abnormalities are detected, test results confirm inflammatory processes in the joints, organs of the urogenital system, kidneys, and liver.
Common symptoms of chronic tonsillitis include:
- frequent exacerbations of tonsillitis in the form of angina (with a simple form – 3-5 times a year) against the background of hypothermia, overwork, fasting, viral or bacterial infection;
dry pharyngeal mucosa, pain, foreign body sensations during swallowing; - periodic (with a toxic-allergic form of the second type – permanent) temperature rise to subfebrile indicators;
presence of bad breath; - increase, soreness of mandibular lymph nodes;
- general fatigue, headaches, decreased body resistance;
- when inspecting the pharynx, hyperemia, thickening, swelling of the palatine arches, tonsils are detected, translucent mucous plaque, lacunary traffic jams are possible.
The exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis is also sometimes called purulent tonsillitis. Exacerbation occurs in the form of bacterial or viral angina. Depending on the type of pathogen, it can be a herpetic sore throat, streptococcal or adenoviral tonsillitis. The disease is accompanied by local manifestations (sore throat, severe swelling, redness of the tonsils and palatine arches, the presence of purulent foci), a sharp rise in temperature, signs of general intoxication of the body (fever, headaches, weakness in muscles, joints, nausea, weakness, etc.) .).
When exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis, symptoms and treatment can vary due to the individual patient’s characteristics, the etiology of the disease, which requires consulting a doctor to differentiate the diagnosis and designate a course of therapy.
Chronic tonsillitis is more characteristic of the childhood age, although it is often observed in adults, differing in the predominance of local symptoms over the general signs of the disease. Chronic tonsillary symptom in adulthood is most often the result of self-treatment of acute illness, tonsillitis, adenovirus infection. The reason may also be the presence of an infectious focus in the oral cavity: gingivitis, caries, etc.
In elderly people, there is a natural process of reducing the volume of lymphoid tissues and a decrease in the concentration of immunocompetent cells, and therefore acute and chronic tonsillitis occurs with absent symptomatology, febrile body temperature and severe pain are rarely observed in the clinical picture in the subfebrile range and signs of general intoxication of the body.
The disease is dangerous by the presence of a permanent source of infection in the body, which contributes to the development of severe disorders in the work of organs and systems. The most frequently observed effects of the rheumatic type, such as:
- rheumatic heart disease;
- rheumatic polyarthritis (with lesions of the synovial membrane of the joint);
- rheumatic fever, affecting the nervous system of the body;
- inflammatory lesions of the skin of a rheumatic nature.
Rheumatism develops under the influence of two factors: the influence of toxins excreted by pathogenic microorganisms on heart tissue and the similarity of antigens of some strains of streptococcus with those inherent in the human body. The second factor causes a pathological systemic autoimmune response, in which immune cells begin to infect their own human cells, perceiving them as foreign. In addition to the general effect on health, the inflammatory process can also develop locally, causing paratonzillity, the formation of retropharyngeal and parapharyngeal abscesses.
Treatment of chronic tonsillitis
Treatment is carried out on an outpatient or home basis. The following methods may be used:
- drug therapy
- washing the tonsils with solutions
- physiotherapy,
- surgery.
Often used combinations of various methods of conservative treatment.
Medication treatment
In the chronic form, treatment with drugs has been recognized as the most effective. Proper selection of drugs helps to conduct effective conservative treatment of tonsillitis in adults and children. Drugs used for the disease are aimed at systemic and local effects, depending on the history, clinical picture of inflammation, the presence of complications and test results.
The group of first choice drugs for exacerbation of chronic forms are antibacterial agents. Their purpose is the maximum possible removal of bacteria from the oral cavity. The exact selection of the antibiotic is carried out according to the results of the assessment of the concentration of pathogenic microorganisms in the contents of the lacunae of the tonsils and their sensitivity to various groups of antibiotics. In 70% of cases, the disease occurs due to damage to the tissues of the tonsils with hemolytic streptococcus, in connection with which penicillin preparations are prescribed most often for its treatment. In case of individual intolerance to drugs of the penicillin group, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. In determining another pathogen of inflammatory disease, the choice of the antibacterial effect of the targeted effect is necessary.
Self-treatment with antibacterial drugs is dangerous not only by its low efficacy, but also by the emergence of tolerance of pathogens to the active substance of the antibiotic, which can significantly complicate the subsequent therapy of the disease.
Antibacterial therapy is not used in the latent form of the disease and during remission. The duration of the course of antibiotic treatment is determined by a specialist. With prolonged therapy with antibacterial agents, broad-spectrum drugs, high doses of medications, in the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, digestive disorders, it is advisable to combine antibiotics with probiotic preparations to restore the intestinal microflora.
It is also possible to use local antibiotics in the form of sprays during mild exacerbations, but the selection of the active substance should be based on the results of the analysis of bacterial seeding. The use of this type of medication is not a basic method of therapy, since the superficial irrigation of the tonsils with an antibacterial composition has a temporary effect and does not contribute to the accumulation of the active substance in the lymphoid tissue. Frequent rinsing with antibacterial agents for the chronic form of the disease is currently recognized as an unjustified treatment method: local exposure is not effective, but may contribute to the formation of antibiotic-resistant flora.
In chronic tonsillitis, it does not make much sense to take antiviral drugs, because in most cases the causative agent of the disease is bacteria.
If chronic tonsillitis is detected, treatment should include other groups of drugs. In case of severe pain in the throat, pain medications of local and general action are prescribed. Tablets of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (nimesulide, ibuprofen, paracetamol, ibuklin) are used for exacerbations of the chronic form of the disease.
Effective therapy is carried out with the help of antiseptic drugs: sprays, solutions for lubricating the throat, rinsing. Antihistamines, used systematically, help reduce the severity of swelling of the palatine arches and tonsils, as well as reduce the overall allergization of the body.
Local, local emollients are used to reduce the discomfort associated with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tonsils and the surface of the pharynx. Most of the finished forms of drugs used for tonsillitis, combine antiseptic, emollient, anti-inflammatory effect. It is possible to use self-made salt solutions, decoctions of herbs with antiseptic action for rinsing, methods of alternative medicine (phytoacelles, herbal preparations) with the recommendation of a specialist and no contraindications.
Since the restoration of general and local immunity is important in the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases, it is possible to prescribe immunostimulant drugs, and also to maintain a healthy lifestyle, with prolonged remission, the body is healed by methods of hardening, playing sports, a full diet, timely rest, exclusion of harmful factors.
Treatment with conservative methods
The methods of conservative therapy offer a wide range of procedures that are part of the overall complex treatment of the chronic form of the disease. In most cases, the methods of conservative therapy with the observance of the rules of treatment are sufficient for the patient to recover.
With a diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis, treatment often includes a method such as washing the lacunae of the tonsils with aseptic solutions. It is considered the most common and widely available method of conservative therapy for tonsillitis. The goal is to remove plaque, lacunar plugs, accumulations of dead epithelium, leukocytes and other tissues and particles lingering inside the lacunae due to sclerotic changes in tissues that prevent the tonsils from clearing themselves. The procedure is carried out with the help of various instruments: the use of a medical syringe with a curved cannula is often used, although less effective. More modern special nozzles make it possible to deliver an aseptic solution under increased pressure and to achieve a complete cleansing of the lacuna. Together with the washing, it is possible to combine the introduction of drugs into the lacunae in the form of a solution through a syringe, a washing nozzle or an ultrasonic device that creates a suspension of antiseptic solution. To achieve the desired therapeutic effect, a course of washing is prescribed on average from 10–12 procedures in combination with treating the surface of the tonsils with Lugol’s solution.
Physiotherapy in the treatment of tonsillitis is a well-known and effective methods in the complex therapy of the disease. The most commonly resorted to ultraviolet irradiation of the region of the tonsils, pharynx with the aim of sanitizing the surface by physical methods, as well as warming the throat. The methods of physical effects include the use of therapeutic laser therapy to reduce edema and severity of inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane and vibroacoustic effects, allowing to improve microcirculation and blood supply in the tissues of the tonsils.
The previously used methods of extrusion and suction of the contents of the lacunas proved low efficiency and increased risk of injury, causing both the spread of inflammation and the acceleration of scar tissue formation. At the moment, these methods are used solely for the purpose of withdrawing content for research.
Comprehensive treatment aimed at reducing the severity of the inflammatory process, tissue regeneration and restoration of the microflora of the tonsils, is conducted by courses. The combination of medical and conservative treatment should be carried out during the period of remission, in the absence of signs of exacerbation. To achieve clinical recovery, therapy is carried out 2 to 4 times a year, depending on the patient’s individual response.
Surgical treatment
For the treatment can also be used operational methods, which consist in the radical surgical removal of the tonsils. Since in this case, the body loses one of the organs of the immune system, it is resorted to when the disease progresses, and conservative methods do not have the desired effect.
The indications for surgical treatment are:
- obstruction of the airways during sleep, interference with nasal breathing, swallowing due to constant swelling of the mucous membranes or growth of the tissues of the tonsils;
replacement of most of the lymphoid tissue of the organ by the connective, which leads to a significant decrease in its functionality; - pathology progression on the background of regular courses of therapy for a year or more;
- pronounced toxic-allergic forms of the disease;
- severe complications: acute rheumatic fever, rheumatic heart disease, glomerulonephritis and others;
- frequent exacerbations of the disease (more than 5 per year) on the background of conservative therapy;
- abscesses in the tonsils.
Surgical removal of the glands eliminates tissue with inflammatory foci, removes the substrate of the disease and leads to a radical cure. However, when removing lymphoid tissue capable of regeneration and healing, the body loses one of the “barrier” organs that resist infection at the entrance to the respiratory tract, therefore, the availability of indications for surgical intervention should be strictly evaluated by experts.
Some other chronic diseases and disorders of the functions of organs and systems with a high risk of decompensation, for example, are considered contraindications for surgical intervention, for example:
- hypertension;
- hemophilia;
- functional disorders of the kidneys, etc.
Temporary contraindications to the operation are considered to be certain diseases of all patients and the physiological conditions of women:
- any acute forms of nasopharyngeal and upper respiratory tract diseases and exacerbations of other diseases (sinusitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, bronhit / “> bronchitis , etc.);
- caries;
- gingivitis, stomatitis , inflammatory processes bacterial etiology in the mouth;
- menstruation period;
- pregnancy.
Surgical intervention is carried out under the influence of local anesthetic drugs in the clinic. The total duration of the tonsil removal procedure takes from several minutes to half an hour, depending on the patient’s age, the duration of the preparatory stage, the stage of tissue growth. The recovery period after surgery lasts from 3-4 days to 7. Modern techniques used for instrumental intervention. The main recommendations of the recovery period are eating food and beverages in the temperature range of 25-30 ° C, making rations in the first days after surgery from mucous porridges, soft, pureed soups, mashed potatoes, exception of spicy, salty, sour, irritating mucous throat foods, as well as increased load on the vocal cords, smoking, any irritating effects on the wound surface s throat to its full healing.